Laboratory spectroscopies
-
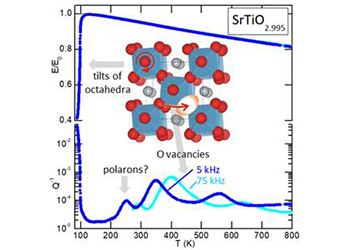
Anelastic spectroscopy
The anelastic spectroscopy measures the strain response to applied stress and is the mechanical analogue to the dielectric spectroscopy (polarization… Read More -
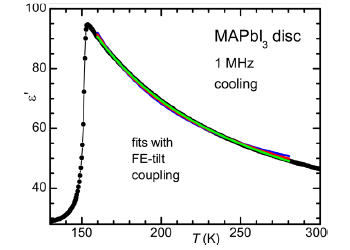
Dielectric spectroscopy
Dielectric spectroscopy measures the response of electrical polarization of a medium to an applied electrical field. It is used for… Read More -
Angle resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES)
Angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) probes the electronic band structure of ordered solids near the Fermi level through the photoelectric effect.… Read More -
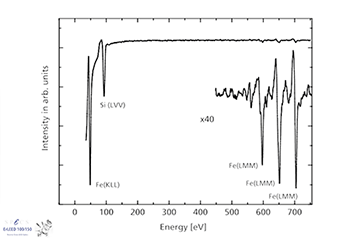
Auger Spectroscopy (AES)
Auger electron spectroscopy (AES) is a surface and element sensitive technique that utilizes a variable high-energy (1-5 KeV) electron beam… Read More -
Electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS)
The EELS is a spectroscopic technique, which permits to measure the energy distribution transferred from an electron beam impinging on… Read More -
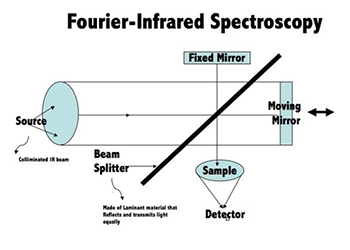
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is considered among the effective techniques to study and understand the chemical and surface chemistry… Read More -
Inverse photoemission spectroscopy (IPES)
The inverse photoemission spectroscopy (IPES) allows to investigate the electronic properties of empty states of solids, surfaces, adsorbate-gas-solid interfaces and… Read More -
Photoluminescence (PL)
Photoluminescence (PL) is the most common characterization technique for materials used for photovoltaic and light-emitting applications. Incident photons are absorbed… Read More -

Raman and micro-Raman spectroscopy
Raman Spectroscopy is a non-destructive chemical analysis technique that provides detailed information about chemical structure, phase and polymorphism, crystallinity and… Read More -
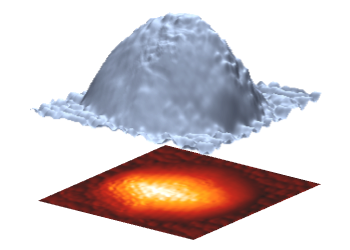
Scanning tunnelling spectroscopy (STS)
Scanning tunnelling spectroscopy (STS) is a technique used in scanning tunnelling microscopy (STM) to probe the local density of states… Read More -

Spectral photoconductivity
The spectral photoconductivity is a powerful tool for measuring the bandgap energy and photoelectronic inter-band transitions in semiconductors, with the… Read More -
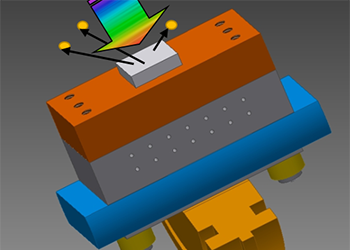
Spectrally resolved total photoemission yield
The spectrally resolved photoemission is a tool for measuring work function of materials and electron affinity of semiconductors. The technique… Read More -
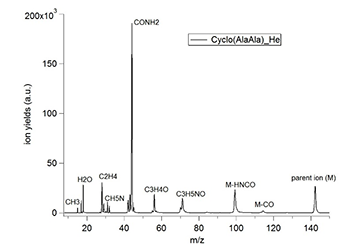
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry (TOF MS)
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge (m/z) ratio of ions. The experiment is performed by… Read More -
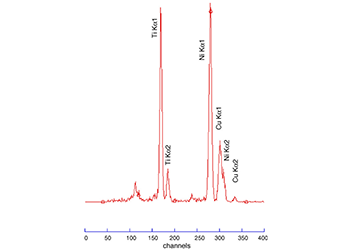
Total X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy (TXRF)
Total X-rays Fluorescence (TXRF) is an ultra-sensitive surface elemental analysis technique. TXRF differs from other XRF techniques by its geometry:… Read More -
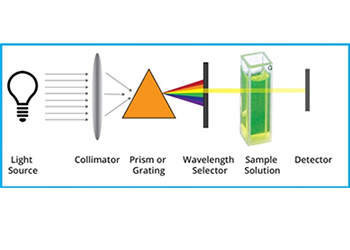
UV-Vis spectroscopy
UV-VIS spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique to determine the optical properties (transmittance, reflectance and absorbance) of liquids and solids.… Read More -
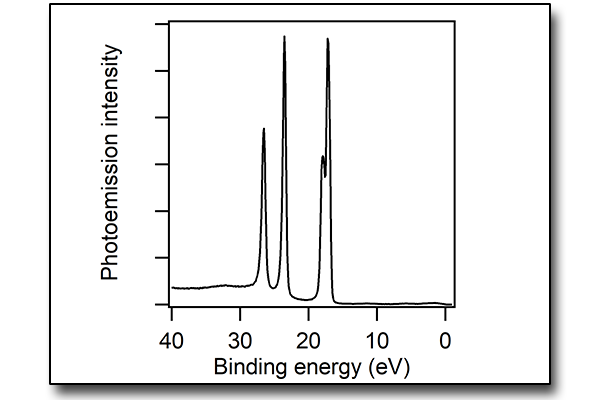
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) studies the chemical properties of solids through the photoelectric effect. In a XPS experiment a solid… Read More
- 1

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)