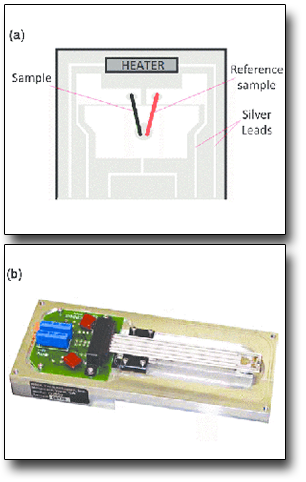
The Seebeck coefficient (S) measurement allows investigating the capability of a material to convert heat to electricity or vice versa. S is a measure of the thermoelectric voltage induced by a temperature difference applied across a material.
The Seebeck coefficient is important for understanding the performance of a material that must be involved in thermoelectric generators or coolers. Moreover, the analysis of the Seebeck coefficient sign allows also to understand the type of the charge carriers involved in the transport of the electrical current induced by the thermal gradient: if S is positive, holes are the main carriers (p-type semiconductors); if S is negative, electrons contribute mainly in the charge diffusion (n-type semiconductors and metals). The generated voltage measurement is performed when applying a thermal gradient between a hot junction and a cold one, and comparing the voltage with the value generated by a reference material operating at the same conditions (e.g. constantan).

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)