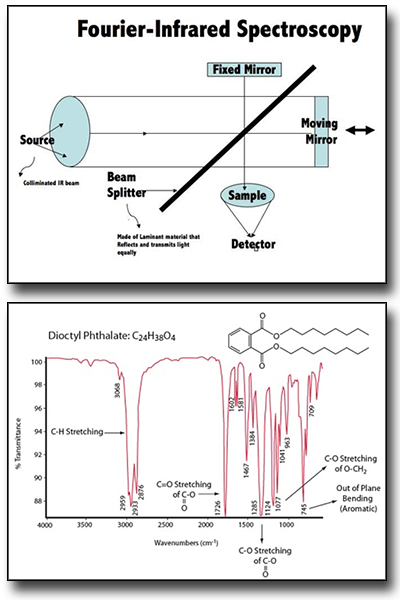
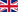
Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is considered among the effective techniques to study and understand the chemical and surface chemistry in various types of materials.
It is a method to determine the structures of molecules collecting a molecular vibrational spectrum. When exposed to infrared radiation, sample molecules selectively absorb radiation of specific wavelengths, which causes the change of dipole moment of sample molecules. Consequently, the vibrational energy levels of sample molecules transfer from ground state to excited state. The frequency of the absorption peak is determined by the vibrational energy gap. The number of absorption peaks is related to the number of vibrational freedom of the molecule. The intensity of absorption peaks is related to the change of dipole moment and the possibility of the transition of energy levels. Therefore, by analyzing the infrared spectrum, one can readily obtain abundant structure information of a molecule.

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)