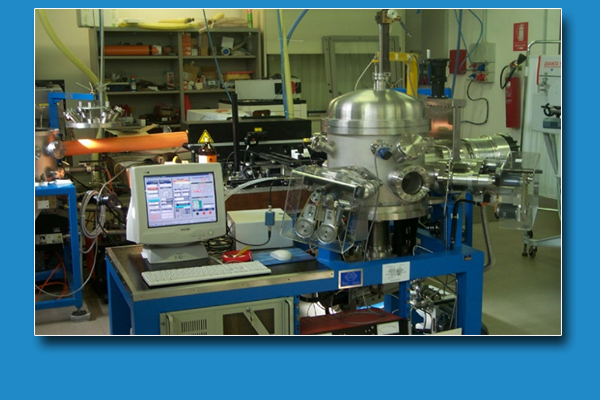
Laser Deposition is a versatile physics technique to obtain functional and advanced materials. It is possible produced thin films, nanostructures and nanoparticles with chemical and physics advanced properties. PLD can be used in biological, organic and inorganic field changing physics laser characteristics. Thin film and nanostructures grow inside high vacuum chamber. X-ray diffraction (Siemens D5000) and Total X-ray Fluorescence (Oxford-Si-Pin) are used, to control chemical and physics properties of news materials. A home-made system for magnetic studies of nanostructured thin films and magnetic nanoparticles by means of magnetooptic Kerr effect (MOKE) in longitudinal geometry is present. The system consists of a photoelastic modulator (PEM), two polarizers, a helium-neon laser, a coil system to generate a magnetic field, a photodiode and the system for data collection and control.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
PLD
- Nd-Yag laser (Time= 10 nanosec, Frequency= 10 Hertz)
- X-Ray diffraction (Siemens D5000)
- Total X Ray Fluorescence (Oxford-Si-Pin)
MOKE
- longitudinal geometry
- He-Ne laser (632 nm)
- magnetic field 800 G
AVAILABLE TECHNIQUES
- PLD
- XRD
- TXRF
- Longitudinal MOKE
SAMPLE
MOKE
-
thin films
-
nanoparticles deposited and/or grown on substrates that do not have magnetic properties
USE FOR
-
Semiconduttori Organici/Inorganici;
-
Thin films/coatings;
-
Nanoparticelle.

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)