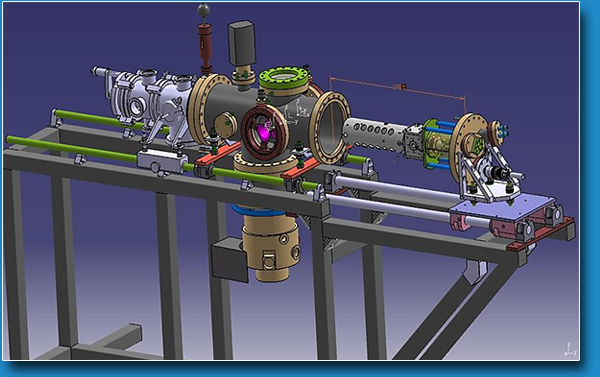
ESI source coupled with a quadrupolar mass spectrometer
Paola Bolognesi -
Jacopo Chiarinelli -
Mass Spectrometry Laboratory
Overview of the electrospray set-up.
From the entrance capillary the ions travel through a skimmer, an octupole ion guide, a quadrupole mass filter (visible in the scheme) and a quadrupolar deflector.
TECHNICAL SPECIFICATIONS
The ESI technique requires small concentrations (10-5 M) of the analyte in mixed solution of water and organic solvents.
- Mass spectrometry.
The quadrupole mass filter (QMS Extrel 2cm rods – 440 KHz radiofrequency) covers the m/z range 4-4000 and can be used as a mass filter (m/z analysis) or in total transmission.
- “Soft lading”.
A deposition chamber is available, with fast entry of the sample and diagnostic tools for the optimization of the deposition conditions. Any conductive material can be used as substrate.
AVAILABLE TECHNIQUES
The apparatus is currently under installation and commissioning.
- Mass spectrometry analysis of different types of compounds an complexes.
- “Soft-Landing” deposition of m/z selected species on conductive substrates and in high vacuum conditions, with control of the kinetic energy of the ions that can be performed after m/z selection.
SAMPLE
The technique is available for molecules and compounds in the mass range between few Da and several tens of kDa. Sample has to be soluble in a mixed solution of water and organic solvent (ethanol, methanol or acetonitrile in typical percentage of 50-20%).
Typical samples are:
-
Small biomolecule (i.e. peptides, nucleobases)
-
Large biomolecules (i.e. proteins and enzymes, DNA strands)
-
Nanoparticles
- Short polymers and biopolymers
Different samples can also be considered and tested for feasibility.
USE FOR
- Spectrometric analysis of unknown compounds for insights into their composition.
- Analysis of complexes formed in liquid solution and their selective binding properties.
-
Deposition under clean conditions (high vacuum) of fragile compounds for conformational characterization.
- Deposition under clean conditions for device fabrication, with or without m/z selection.

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)