Publications
Surface Defect Engineering in Colored TiO₂ Hollow Spheres Toward Efficient Photocatalysis" is among the "Top Viewed Articles" in Advanced Functional Materials.
Wiley, the publisher, has informed us that our work “Surface Defect Engineering in Colored TiO₂ Hollow Spheres Toward Efficient Photocatalysis” ranked among the top 10% of the most viewed articles published by the journal in 2023. This important recognition rewards the value of our research and confirms the interest it has generated within the scientific community.
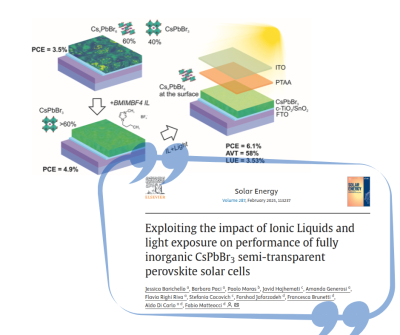
Exploiting the impact of Ionic Liquids and light exposure on performance of fully inorganic CsPbBr3 semi-transparent perovskite solar cells - New article
In this article published in Solar Energy, the result of a collaboration between CNR-ISM, the University of Tor Vergata, and Institut Photovoltaïque d'Île-de-France, the focus is on CsPbBr3 perovskite, a promising material ideal for photovoltaic devices.
Its semi-transparency paves the way for various innovative applications, such as solar windows, agrivoltaic solutions, and indoor energy-harvesting devices. However, to compete effectively in the market, improving its efficiency is essential.
By employing an ionic liquid, the fabrication process has been optimized, leading to a significant increase in overall conversion efficiency. This advancement marks a crucial step forward in the development of more efficient and versatile photovoltaic technologies.
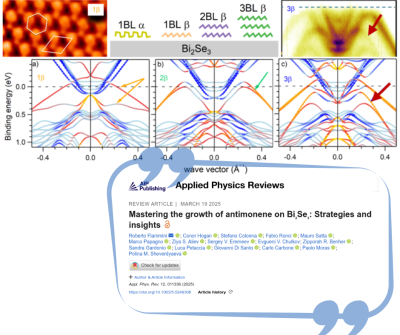
Mastering the growth of antimonene on Bi2Se3: strategies and insights - New paper
In this study, a combination of DFT and atomistic thermodynamic calculations, STM microscopy, XPS, and ARPES was employed to precisely determine the conditions required for the controlled growth of one, two, or three ordered layers of β-antimonene. Additionally, researchers analyzed how the material's electronic and chemical properties vary depending on the thickness.
These findings could pave the way for advanced technologies, including nanoscale electronic devices, sensors, and energy systems.
The study was published in Applied Physics Reviews.
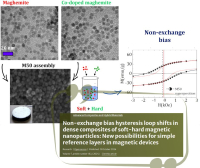
Engineering hard ferrite composites by combining nanostructuring and Al³⁺ substitution: From nano to dense bulk magnets – A new Paper on Advancements in Permanent Magnets
The study focuses on the sol-gel synthesis of SrFe₁₂O₁₉/CoFe₂O₄ nanocomposites for high-coercivity permanent magnets using scalable methods.
The research investigates how morphology, structure, and composition influence magnetic properties: cation substitution and super-exchange coupling at the interface modulate hysteresis; Monte Carlo simulations confirm the key role of crystallite size and epitaxial growth; the Spark Plasma Sintering technique enhances magnetic performance by optimizing material design.
Article published in Acta Materialia.
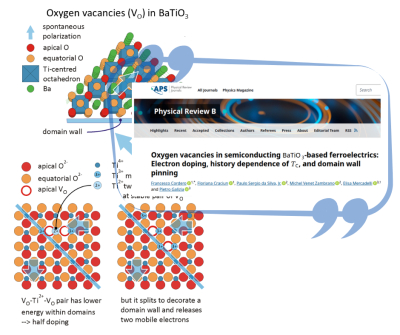
Oxygen vacancies in semiconducting BaTiO3-based ferroelectrics: Electron doping, history dependence of Tc, and domain wall pinning - New article
Oxygen vacancies (VO) are a major cause of degradation in devices based on materials of the BaTiO3 type. We measured the complex Young’s modulus vs T,f of BaTiO3 and similar samples with controlled amounts of VO. The VO are probed through the absorption peaks vs T due to their hopping, and through the dependence of the Curie temperature on aging. Tc is mainly depressed by the mobile electrons doped by the VO, whose number is reduced by VO aggregation into pairs. A long time decrease of Tc is due to the dissociation of pairs to decorate domain walls, which is possible only as isolated VO.
Article published in Physical Review B.
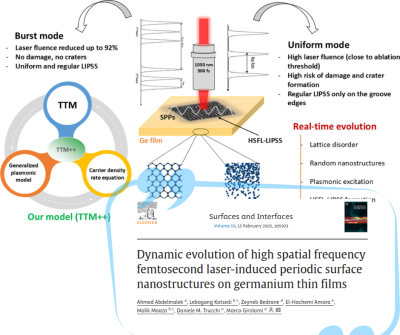
Dynamic evolution of high spatial frequency femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface nanostructures on Germanium thin films - New article
The paper presents a comprehensive theoretical study of the mechanisms underlying the formation of high-spatial-frequency periodic nanostructures (HSFL-LIPSS) induced by 300 fs laser pulses on crystalline Germanium thin films, allowing to identify the physical phenomena that occur in the very early stages of the process.
In particular, HSFL-LIPSS are due to ultrafast processes such as non-thermal melting, in which the material lattice remains cold despite the change of state.
Article published in Surfaces and Interfaces.
On-Surface Synthesis of Carbaporphyrinoid-Based Polymers - New article
New two-dimensional polymers based on porphyrinoid structures have been successfully synthesized, offering promising prospects for electronic, optical, and catalytic applications. This breakthrough was achieved through precise molecular design, incorporating controlled carbon-carbon couplings, halogen-functionalized precursors, and cobalt atom coordination.
The study, conducted under ultra-high vacuum conditions, utilized surface-assisted synthesis to create both one-dimensional (1D) and two-dimensional (2D) carbaporphyrinoid polymers.
Article published in Small.
Multiple Reaction Pathways for Oxygen Evolution as a Key Factor for the Catalytic Activity of Nickel−Iron (Oxy)Hydroxides - New Article
"We used DFT simulations to study the structural and electrochemical properties of iron-doped nickel (oxy)hydroxide catalytic films for water oxidation, a crucial process for the production of E-fuels. Our results confirm the data obtained with X-ray absorption spectroscopy, highlight the role of concerted proton-electron transfers in oxygen production reactions, and show that iron enhances the catalytic activity of nickel-based catalysts by reducing the potential required for the formation of key intermediates."
Article published in Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Origin and Potentialities of the Selective Host-Matrix Effect in Hydrogenated III-V-N Alloys - New Article
InGaAsN alloys are a widely studied class of materials, useful in the design of devices where band gap modification, whether general or localized, can lead to the production of low-dimensional quantum phenomena.
New Exotic Magnetic Phenomena - New article published in Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials
Exchange bias is widely studied in thin films and nanoparticle composites, but the role of non-exchange mechanisms in hysteresis loop bias remains unclear. Dense soft-hard binary nanoparticle composites provide insights into dipolar interactions' effects on loop shifts and offer a way to enhance bias in magnets with asymmetric magnetization reversal. Such a “dipolar bias" is experimentally and theoretically demonstrated, introducing new methods to tune hysteresis in hybrid systems.
More...
Double-pentagon silicon chains in a quasi-1D Si/Ag(001) surface alloy - New Article
The structure of the submonolayer Si/Ag(001) surface has been solved, almost two decades since the first studies appeared, thanks to an international collaboration involving researchers from CNR-ISM Rome.
Using a combination of density functional theory, scanning tunnelling microscopy, and grazing incidence x-ray diffraction simulations, the researchers demonstrated a double pentagon chain structure formed within a Si/Ag surface alloy. The results, which confirm the importance of pentagonal geometries in 2D materials and surface alloys, are published in Nature Communications.
Energy and charge transfer observed in real time - A new paper
An international collaboration that involved researchers from eight different institutions (Department of Physics Polytechnic of Milan, CNR-IFN, CNR-ISM, IMDEA Nanociencia, Departamento de Quimica UAM, Departamento de Quimica Organica Universidad Complutense de Madrid, imec Louvain and Sincrotrone Trieste ) reported for the first time the measurement of the time necessary to transfer the charge from an electron donor system to the adjacent carbon atom in a benzene ring and therefore the time in which the structural change of the molecule occurs.
The results are published in Nature Chemistry.
Ultrafast Dynamics of Nonthermal Carriers Following Photoexcitation of palsmonic nanostructure - A new paper
An article on the different dynamics of nonthermal carrier generation in two-dimensional arrays of gold nanoparticles, following their photoexcitation at the plasmon resonance or the interband transition, has been published in ACS Photonics: "Ultrafast Dynamics of Nonthermal Carriers Following Plasmonic and Interband Photoexcitation of 2D Arrays of Gold Nanoparticles."
The publication is the result of a collaboration between the EFSL research group at CNR-ISM and researchers from CNR-SPIN, CNR-IFN, the Università di Genova, and the Politecnico di Milano.
Spin-Dependent ππ* Gap in Graphene on a Magnetic Substrate - A new paper
A study on the electronic properties of the Graphene/Ni(111) system intercalated with a monolayer of Eu has been conducted by a group of CNR-ISM researchers and published in Physical Review Letters, selected as an Editor’s Suggestion.
This system allows for the induction of spin polarization in graphene while simultaneously maintaining its electronic characteristics nearly unchanged. Angle-resolved and spin-resolved photoemission spectroscopy (ARPES) measurements, combined with DFT calculations, show that the system retains the linear dispersion of the graphene Dirac cones, despite the presence of the strongly interacting Ni substrate.






 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)