The EELS is a spectroscopic technique, which permits to measure the energy distribution transferred from an electron beam impinging on the sample, analyzing the electron energy loss, which have done anelastic scattering. There are two classes of EELS: TEELS and REELS. In TEELS the analysed electrons are transmitted through the sample, in REELS they are reflected.
The electrons of the primary electron beam interact with solid exchanging energy and momentum and in this way excite the oscillation mode characteristic of lattice (phonons), and of electron gas of quasi free electrons (plasmons), or they promote the electronic transitions among energetic bands into the solid (excitation of electrons into unoccupied energy levels in the conduction band). Thus, varying the energy of the primary electron beam it is possible to excite different transitions.
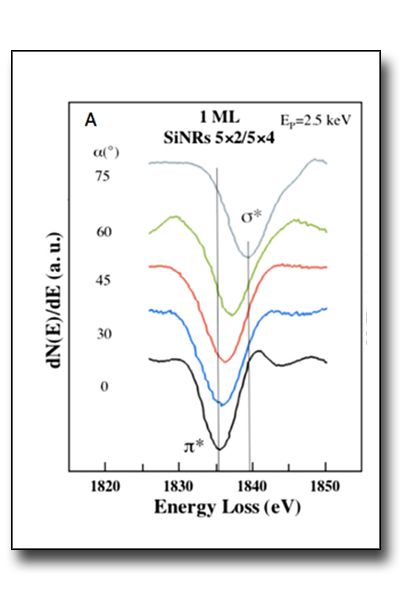
The REELS spectroscopy is spatially dependent due to the shape of the orbitals involved into the electronic transitions

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)