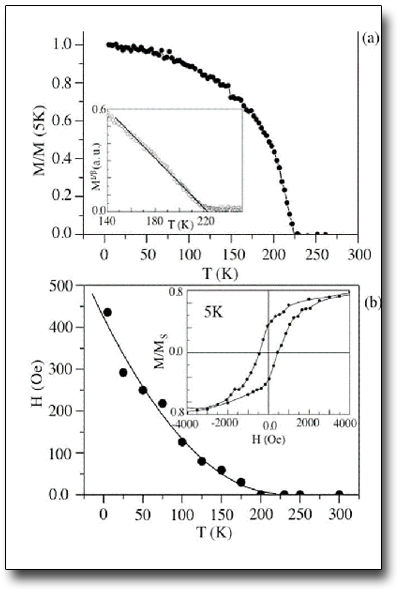
A SQUID (Superconducting Quantum Interference Device) is a very sensitive magnetometer used to measure extremely subtle magnetic fields, based on superconducting loops containing Josephson junctions. The RF sQUID device acts as a magnetic flux to voltage converter, detecting the change of magnetic flux created by mechanically moving the sample through a superconducting second order gradiometer pick-up coil (to suppress the influence of all kinds of external magnetic fields); such change is finally converted to a voltage (VSQUID) profile from which the magnetic moment can be unfolded by a fit assuming the dipole approximation. The SQUID magnetometer allows the characterization of magnetic thin films and nanoparticles (in powder or dispersed in liquids) in a wide range of temperature (4K < T < 400K ) and applied field ( Hmax = 5.5 T).

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)