Electrochemical analysis uses electrically conductive probes or electrodes which are usually linked to electronic devices that measure the electrical parameters generated by the redox reaction of the species in solution. The electroanalytical techniques usually use three electrodes, known as the working electrode, the reference electrode and the counter (auxiliary) electrode. These electrodes are connected to a potentiostat that controls the working electrode potential and determines the resulting current providing information about the electrical parameters of the reactants in solution.
Cyclovoltammetry
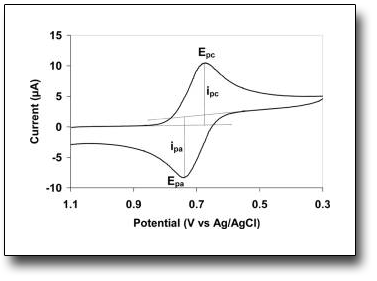
The Cyclovoltammetry (CV) is an electrochemical technique based on the application of a potential to a stationary electrode immersed in an unstirred solution. In a common experiment, a variation of potential is imposed on a working electrode and the contextual variation of current is recorded. The potential varies linearly with a speed called" scan speed", generally measured in volts per second (V / s). The measuring cell typically has 3 electrodes immersed in the solution of the electroactive compound and a supporting electrolyte. The potential is measured between the reference electrode, with constant potential, and the working electrode, while the current is measured between the working electrode and the counter electrode; the current (i) is reported against the applied potential (E) to give the so-called cyclevoltammogram. As the potential changes for each compound that can be reduced (or oxidized) there will be an exchange of electrons with the working electrode, so as to give a variation of the measured current which produces a peak in the voltammogram. If the process is reversible, by inversion of the applied potential, the product formed in the first part of the scan will be re-oxidized (or reduced) producing a current of opposite polarity. The new peak of the voltammogram will have a shape similar to the previous one but with reverse polarity. From this it is possible to derive the redox potential and the speed of the electrochemical reaction that took place.
PalmSens4
Autolab PGStat 204

 English (UK)
English (UK)  Italiano (Italia)
Italiano (Italia)